Hello guys!
I am working on an application that needs to display certain amount of items in a a scrollable view that have headers on top of every one of them, so as the title says, RecyclerView.
However, my data that is coming from SQLite backed database didn’t fit too well on the mould of just using different kind of view types, because the data was coming from SQLite on demand and if I were to use view types to support headers I would have to process the whole database before showing it and add some kind of layer that provides me with the headers.
After couple of quick googles I found couple of promising libraries , but unfortunately for my need, they didn’t have support for GridLayout or required same kind of view type mapping as regular headers, but I wouldn’t give up now, as I knew RecyclerView provides lovely way of adding custom decorations, which were used to implement timeshops sticky headers, and after studying the code of other implementations I was ready to go!
But first I needed to make my own SpanSizeLookUp implementation to separate different sections of the grid.

So the basic idea is that last item of each section is given with a span that makes it fill the rest of the row, so that the next sections items are dropped to the next row.
First I needed the information of which item belongs to which section, which I made my StickyGridHeadersAdapter in similar fashion as in timeshops implementation.
So the primary function of the adapter is to provide the header id for each position and its corresponding view.
So now that I got the information I am ready to extend the SpanSizeLookUp!
SpanSizeLookUp has one important function of determining each items span size, which is done by implementing getSpanSize method that takes the position of them item as parameter.
My implementation of getSpanSize first determines whether the item in question is the last item before next header, and if so, it calculates the remaining amount of columns in that row, that it needs to fill in order to bump the following item to next row.
So first we implement the last item before next header check, which is quite simple, take current and next item, and if their ids are different, they belong to different categories, meaning that the item in question is actually the last item before next header! Pretty simple huh?
/**
* checks if item is last before next header
* <p/>
* aka if next items id is different than current
*
* @param itemPosition
* @return
*/
private boolean isLastBeforeNextHeader(int itemPosition) {
//header id of item in question
long headerId = adapter.getHeaderId(itemPosition);
//next header id, -1 if out of bounds, aka the rest of the row must be filled!
long nextHeaderId = -1;
//next item position, aka next item in question
int nextItemPosition = itemPosition + 1;
//checking if is within the bounds of the adapter
if (nextItemPosition >= 0 && nextItemPosition < adapter.getItemCount()) {
nextHeaderId = adapter.getHeaderId(nextItemPosition);
}
//checking if the ids different
return headerId != nextHeaderId;
}
Then we need to implement the actual span size lookup, it needs a little bit more logic!
@Override
public int getSpanSize(int position) {
if (isLastBeforeNextHeader(position)) {
//gets the number of items before this particular position in range of 0..spancount - 1
int categoryOffset = getNumberOfItemsBeforePositionInCategory(position);
//gets column index in range of 0..spancount - 1
int columnIndex = (categoryOffset % spanCount);
//gets number of extra columns in range of 0..spancount - 1
int extraColumns = spanCount - (columnIndex + 1);
return 1 + extraColumns;
} else {
//is just any ordinary item, takes one column width..
return 1;
}
}
So first we use our lastly implemented method and check if it actually is the last item within the section, and if not, just return one.
But if the case is different, aka if it is the last item, we first calculate the offset of this item in question within the section, which is needed to calculate the remaining columns within the row, but for that we need to implement a way to calculate those preceding items.
Fortunately for us, its quite simple chore, given the fact that we can query the header id of each item, so basically what we do is we loop through each item preceding the current item til we find a change in header id!
private int getNumberOfItemsBeforePositionInCategory(int position) {
long categoryId = adapter.getHeaderId(position);
for(int i = 1; i < position; i++) {
if(adapter.getHeaderId(position - i) != categoryId) {
return i - 1;
}
}
return position;
}
And to account for the case that this happens to be within the first category, we just return the given position, as it is the offset to the start of the list.
So with that info we can now calculate the column index..
//gets column index in range of 0..spancount - 1 int columnIndex = (categoryOffset % spanCount);
which is just taking modulus of the offset within category and the span count
and to get the amount of items there are left on this row after the particular item, we just substract the column index + 1 from the span count, accounting for the the range of 0.. span count – 1 of the columnIndex instead of 1 – span count
//gets number of extra columns in range of 0..spancount - 1 int extraColumns = spanCount - (columnIndex + 1);
so then we can just return the amount of columns that this is supposed to fill, meaning one plus the amount of extra columns
return 1 + extraColumns;
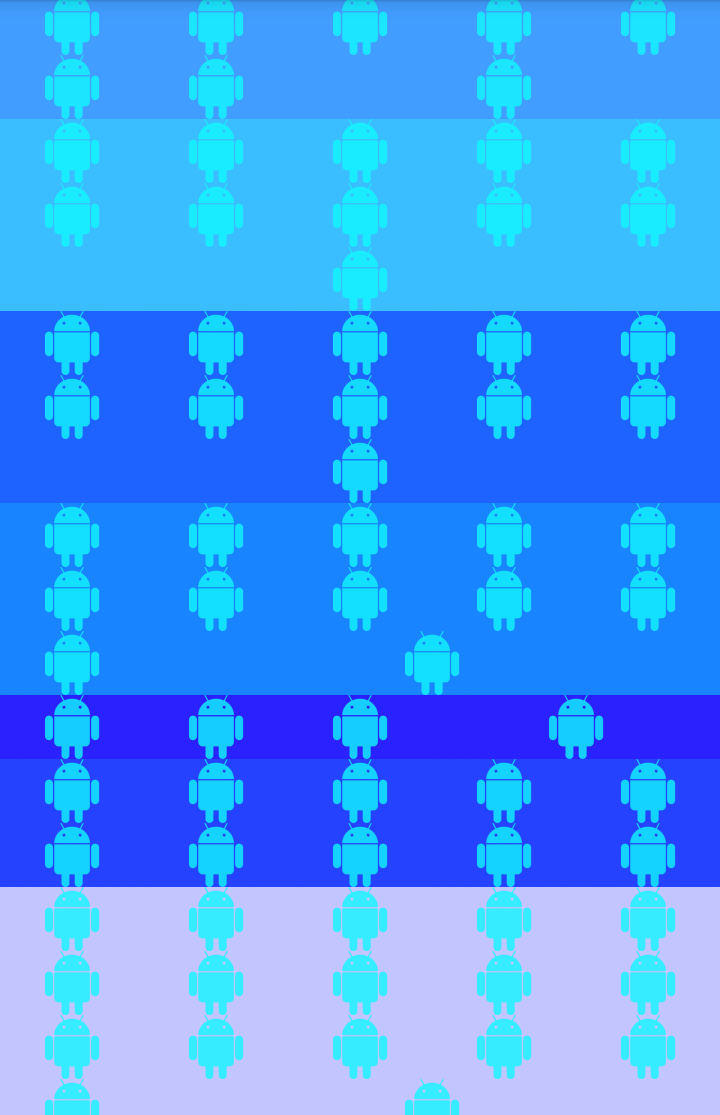
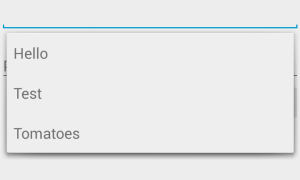
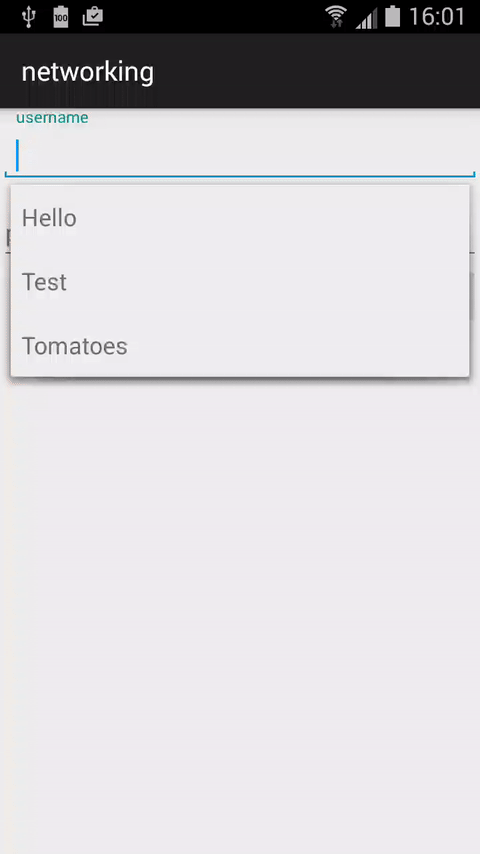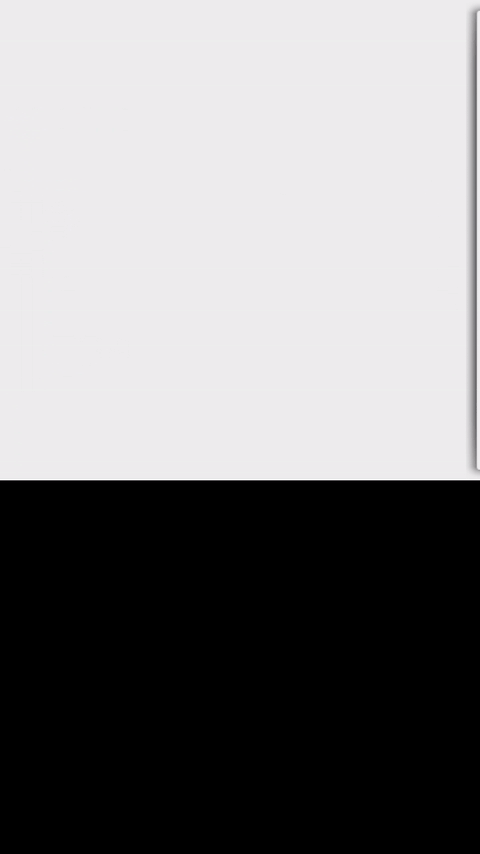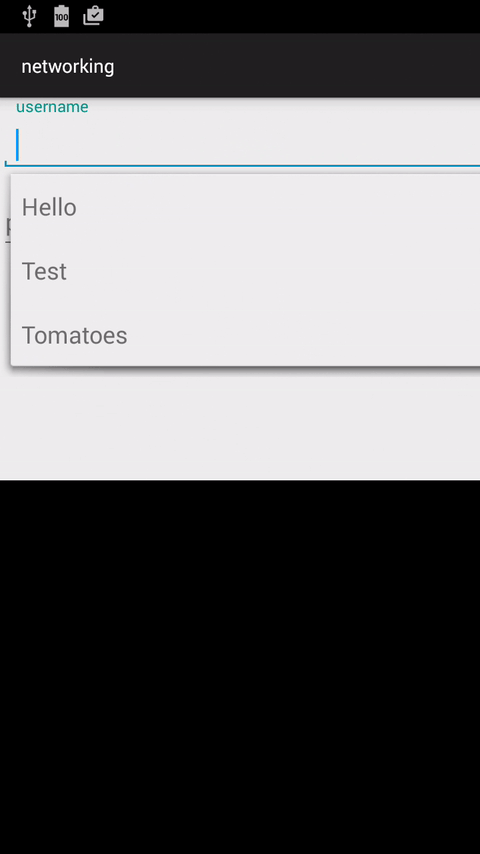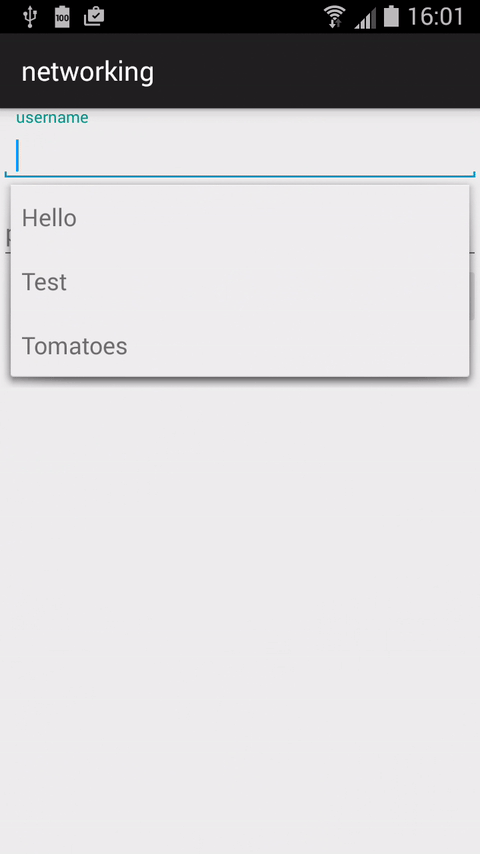
So now if we run the code, what we can see, is that each category is withing its own boundaries, cool!
This may not be obvious from the preview above, but if you look closely the last item within each section(read: color) is spanning to fill the rest of the row.
Now we only need to add the headers for each section, let the fun begin!
So we need to implement RecyclerView.ItemDecoration, which has two important methods, onDrawOver to draw over the RecyclerView, which handles the drawing of the header view, and getItemOffsets, which provides the offsets to the views, giving enough space for the header in this case, but the possibilities are limitless!
So first lets give enough space for the headers by implementing getItemOffsets!
@Override
public void getItemOffsets(Rect outRect, View view, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) {
super.getItemOffsets(outRect, view, parent, state);
int itemPosition = parent.getChildAdapterPosition(view);
if (itemPosition == RecyclerView.NO_POSITION) {
return;
}
boolean underHeader = isUnderHeader(itemPosition);
if (underHeader) {
View header = getHeaderView(parent, itemPosition);
outRect.top = header.getHeight();
}
}
This method in my case only checks if the item is under header, and if so, gives it top padding from the header height
To determine if item is under header we use isUnderHeader method which is implemented as follows:
private boolean isUnderHeader(int itemPosition) {
return isUnderHeader(itemPosition, spanCount);
}
/**
* checks if item is "under header"
* <p/>
* Items is under header if any of the following conditions are true:
* <p/>
* a) within spanCount the header id has changed once
*
* @param itemPosition
* @return
*/
private boolean isUnderHeader(int itemPosition, int spanCount) {
if (itemPosition == 0) {
return true;
}
//get current items header id
long headerId = adapter.getHeaderId(itemPosition);
//loop through each item within spancount
for (int i = 1; i < spanCount + 1; i++) {
long previousHeaderId = -1;
int previousItemPosition = itemPosition - i;
//gets previous items headerId
if (previousItemPosition >= 0 && previousItemPosition < adapter.getItemCount()) {
previousHeaderId = adapter.getHeaderId(previousItemPosition);
}
//checks if header id at given position is different from previous header id and if so, returns true to indicate this item belongs under the header
if (headerId != previousHeaderId) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
We just loop the range of span count and check if there’s any item that has different header id than the given position, and if so, we know that this item belongs under header and needs to be given space!
now we can implement the drawing of the header, this function is a bit more exotic to handle the stickiness of headers, meaning moving the topmost header upwards when it is pushed by the following header.
@Override
public void onDrawOver(Canvas c, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) {
super.onDrawOver(c, parent, state);
final int childCount = parent.getChildCount();
//checks if there's any childs, aka can we even have any header?
if (childCount <= 0 || adapter.getItemCount() <= 0) {
return;
}
//stores the "highest" seen top value of any header to perform the pusheroo of topmost header
int highestTop = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
//loops through childs in the recyclerview on reverse order to perform the pushing of uppermost header faster, because before it, there is the next headers top stored to highestTop
for (int i = childCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
View itemView = parent.getChildAt(i);
//fetches the position within adapter
int position = parent.getChildAdapterPosition(itemView);
if (position == RecyclerView.NO_POSITION) {
continue;
}
//only draw if is the first withing recyclerview, aka is the first view in whole tree or if the item in question is the first under its category(or header..)
if (i == 0 || isFirstUnderHeader(position)) {
//fetches the header from header provider, which is basically just call to adapters getHeader/bindHeader
View header = headerProvider.getHeader(parent, position);
//calculates the translations of the header within view, which is on top of the give item
int translationX = parent.getLeft();
int translationY = Math.max(itemView.getTop() - header.getHeight(), 0);
tempRect.set(translationX, translationY, translationX + header.getWidth(),
translationY + header.getHeight());
//moves the header so it is pushed by the following header upwards
if(tempRect.bottom > highestTop) {
tempRect.offset(0, highestTop - tempRect.bottom);
}
//draws the actual header
drawHeader(parent, c, header, tempRect);
//stores top of the header to help with the pushing of topmost header
highestTop = tempRect.top;
}
}
}
so first we perform couple of sanity checks to avoid useless drawing, we check if there actually is any items within the RecyclerView and if not, we just return to avoid useless work
final int childCount = parent.getChildCount();
//checks if there's any childs, aka can we even have any header?
if (childCount <= 0 || adapter.getItemCount() <= 0) {
return;
}
then we initialize the value to store the preceeding headers top value to perform the pusheroo of topmost header, as commented
//stores the "highest" seen top value of any header to perform the pusheroo of topmost header int highestTop = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
then for each item in backward order we do the following:
check if header should be drawn, by checking if is first item, which always should show header, making the sticky header effect, or if is first under any header
if (i == 0 || isFirstUnderHeader(position)) {
and the checking if the item is last header is quite simple, we just check if the preceding item has different header than current
private boolean isFirstUnderHeader(int position) {
return position == 0 || adapter.getHeaderId(position) != adapter.getHeaderId(position - 1);
}
and the item is first in the whole RecyclerView or first within its category, we now know that we can draw the header for this particular item, so we do that!
first we get the header item
//fetches the header from header provider, which is basically just call to adapters getHeader/bindHeader View header = headerProvider.getHeader(parent, position);
which works in similar fashion as in timeshops implementation, we just call adapters get/bind header methods to obtain the header bound for this header id
then we just calculate the translations for this header, to draw it on top of the item in question
//calculates the translations of the header within view, which is on top of the give item int translationX = parent.getLeft(); int translationY = Math.max(itemView.getTop() - header.getHeight(), 0);
then we set these values for a rect to pass them around and to more easily apply moving when translation topmost header to give room for the next
tempRect.set(translationX, translationY, translationX + header.getWidth(),
translationY + header.getHeight());
Then we adjust the rect position if it is pushed by the following header, aka if the current headers bottom is smaller than highest top, meaning the previously processed headers top
//moves the header so it is pushed by the following header upwards
if(tempRect.bottom > highestTop) {
tempRect.offset(0, highestTop - tempRect.bottom);
}
then we actually draw the header
//draws the actual header drawHeader(parent, c, header, tempRect);
and what this method call does is just draws the view on the given canvas within the rect
public void drawHeader(RecyclerView recyclerView, Canvas canvas, View header, Rect offset) {
canvas.save();
canvas.translate(offset.left, offset.top);
header.draw(canvas);
canvas.restore();
}
and then just set the highestTop to current headers top
//stores top of the header to help with the pushing of topmost header highestTop = tempRect.top;
and I think we’re about to be done here!
After a quick run we can see it works as expected!
However this is just a simple and quick implementation and we might be missing something here, but for my simple use case it works, and if I find out anything, I’ll update here!
Should of probably used thicker header on the preview but… meh!
Thanks for reading anyway!